Power BI Report Server: Key Features and Elements
Every CTO knows the struggle of managing complex reports. The inefficiency of scattered data, the constant juggling between reporting tools, the challenge of ensuring accurate KPIs...
Vinod Satapara - December 03, 2024
Listening is fun too.
Straighten your back and cherish with coffee - PLAY !

Do you know when geospatial analysis took traction in healthcare? It was when John Snow, a London-based physician, used it to analyze the spread of cholera, which ultimately proved not to be an air-borne disease but contaminated water.
By then, this ground-breaking technology took hype, breaking the barriers of traditional methods and paving the way for data-driven solutions.
Incorporating spatial data analysis into healthcare decision-making allows for more efficient planning and response to health issues. It can help:
Spatial data analysis involves studying the location and distribution of health-related data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. Given below are some of the ways geospatial analysis improves healthcare processes.
Spatial data analysis helps healthcare systems identify areas with the highest demand for services, allowing for more effective distribution of resources. By mapping out healthcare needs, such as the prevalence of diseases or the density of healthcare facilities, decision-makers can prioritize regions that require additional attention, staff, or medical supplies.
This targeted data visualization approach ensures that resources, like hospital beds, medications, or personnel, are allocated where they are most needed. It also helps prevent resource shortages in high-demand areas and reduces waste in regions with lower healthcare needs, improving overall efficiency and service delivery.
Location intelligence in healthcare helps you pinpoint areas where healthcare services are lacking or inaccessible. By examining the geographic distribution of healthcare facilities, population density, and health outcomes, you can easily identify regions with insufficient medical resources or poor healthcare infrastructure.
Hire Power BI developers from iFour and make the most out of your data
This information allows healthcare providers and policymakers to visualize data, and address gaps in service, ensuring that underserved areas receive the attention they need.
It can lead to decisions such as building new clinics, offering mobile health services, or improving transportation options, ultimately ensuring that all communities have access to quality care.
Geospatial healthcare data analysis can help tailor healthcare services to the specific needs of different communities by considering geographic and environmental factors.
For example, it can reveal patterns in health conditions that are more common in certain areas, such as respiratory issues in urban environments or waterborne diseases in rural areas. This allows healthcare providers to offer more targeted treatments and preventive measures.
Geospatial insights help you:
Location intelligence or simply spatial analytics can be a powerful tool in predicting and preventing disease outbreaks. This helps you identify patterns and trends over time.
By combining geographic information with health data, such as the spread of infectious diseases or environmental factors, healthcare consultants can anticipate where outbreaks are likely to occur. This early warning allows for quicker responses and better preparation.
Using spatial analysis, healthcare systems can track disease hotspots and detect potential risks before they escalate. This proactive approach helps allocate resources, deploy medical teams, and implement preventative measures in high-risk areas, ultimately reducing the impact of outbreaks on public health.
Spatial data analysis plays a crucial role in planning effective emergency responses by mapping out areas most at risk during a crisis. Whether it’s a natural disaster, disease outbreak, or mass casualty event, understanding the geographic layout of affected regions helps emergency teams respond more quickly and efficiently.
This data can highlight areas with high population density or limited access to healthcare, allowing for better coordination of resources.
By analyzing real-time location data, healthcare providers can prioritize affected areas, deploy emergency services where they’re needed most, and reduce response times.
This strategic approach ensures that critical care reaches vulnerable populations faster, improving outcomes and minimizing the impact of emergencies on public health.
Drive innovation through Power Platform consulting services
Spatial data analysis helps track and monitor public health trends by mapping disease patterns, health behaviors, and environmental factors over time.
By analyzing geographic data, health authorities can identify areas with rising health concerns, such as increased cases of specific illnesses or environmental hazards and take proactive measures to address them.
This approach enables continuous monitoring of public health at local, regional, and national levels. It helps identify emerging health threats, track the effectiveness of health programs, and allocate resources more efficiently.
Ultimately, spatial data empowers healthcare systems to respond faster and more accurately to public health needs.
Take a look at these prime Power BI use cases we've crafted for our industry CTOs. These BI examples helped them simplify their operational decisions!
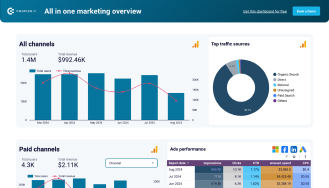
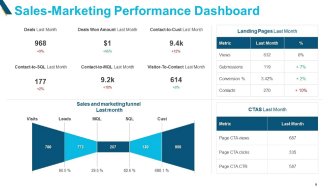
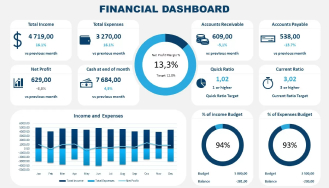
Spatial data analysis helps optimize healthcare facility planning by identifying areas with the greatest need for services.
By analyzing population density, disease prevalence, and existing healthcare infrastructure, planners can determine the best locations for new clinics, hospitals, or specialized care centers, ensuring they are accessible to those who need them most.
This approach allows for better distribution of healthcare resources, reducing overcrowding in certain areas and improving access in underserved regions.
With spatial insights, healthcare systems can ensure that facilities are strategically placed to provide timely care, improve patient outcomes, and use resources more efficiently.
Spatial data analysis is essential for managing population health by helping identify health trends and risk factors within specific communities.
By mapping out health data, such as disease rates, social determinants of health, and access to healthcare, health authorities can better understand the unique needs of different populations.
This targeted approach allows for the development of tailored health programs and interventions that address the specific health challenges of each region. With spatial insights, healthcare providers can improve preventive care, reduce health disparities, and enhance overall population health by allocating resources and services where they are most needed.
Spatial data analysis helps improve patient access to healthcare by identifying areas with limited healthcare facilities or services. By mapping the distribution of clinics, hospitals, and specialists, healthcare providers can pinpoint regions where patients may face challenges in accessing care, whether due to distance, transportation, or resource shortages.
With these insights, healthcare systems can take steps to bridge the gap, such as establishing new facilities in underserved areas, offering telehealth options, or improving transportation networks.
Supercharge your processes with custom healthcare software development
This ensures that patients, regardless of their location, can receive timely and effective care, ultimately improving health outcomes and reducing disparities in access to healthcare.
Spatial data analysis plays a key role in enhancing healthcare equity by highlighting disparities in access to care and health outcomes across different geographic areas. By examining factors like income, education, and healthcare availability, it becomes easier to identify vulnerable populations who may be underserved or face barriers to quality care.
With this information, healthcare systems can develop targeted initiatives to address these inequities, such as increasing access to healthcare facilities in underserved areas, offering mobile health services, or improving outreach programs.
This approach ensures that all communities, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status, receive the care and resources they need to achieve better health outcomes.
Geospatial data analysis in healthcare helps you reduce costs by identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource allocation. By analyzing geographic data on disease prevalence, facility locations, and patient demographics, healthcare systems can ensure that resources like staff, equipment, and facilities are used where they are most needed, avoiding unnecessary spending.
Additionally, by predicting health trends and identifying at-risk populations early, spatial analysis supports preventive care initiatives that reduce the need for costly emergency treatments or hospitalizations.
This proactive approach not only lowers healthcare costs but also improves patient outcomes by addressing health issues before they escalate.
Spatial data analysis supports clinical research by providing insights into how geographic and environmental factors influence health outcomes. Researchers can use spatial data to identify patterns in disease distribution, track the spread of conditions, and explore correlations between health and location, helping to design more targeted studies.
By integrating spatial data into clinical trials, researchers can better understand population health and ensure their findings are relevant to specific communities.
This approach enhances the accuracy of research results, leading to more effective treatments and interventions tailored to the unique needs of different populations.
Automate business workflows with a leading Power Automate consulting company
Spatial data analysis improves environmental health monitoring by mapping the relationship between environmental factors and health outcomes. By tracking variables like air quality, water pollution, or exposure to hazardous materials, health authorities can identify areas where environmental risks may be impacting public health.
This geographic approach allows for more proactive monitoring, enabling quick responses to potential environmental threats.
With accurate GIS data, interventions can be better targeted to reduce health risks in vulnerable areas, leading to improved environmental health and better long-term well-being for communities.
Spatial data analysis enhances disaster response by providing real-time information on the affected areas, including the extent of damage, population density, and accessibility of resources.
By mapping out disaster zones, emergency teams can quickly identify critical areas that need immediate attention, ensuring a more coordinated and effective response.
Read More: Top Data Analytics Trends You Can't Ignore
During recovery, spatial data helps track progress, assess infrastructure damage, and prioritize rebuilding efforts. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are directed to the most impacted areas, accelerating recovery and minimizing the long-term impact on communities.
So, that’s how this data-driven approach takes your healthcare analysis to the next level. I hope you found this article useful.
Maximize your business intelligence with our top-rated Power BI consulting services. Contact us today!
(Turning insights into various data visualizations)
In conclusion, spatial data analysis plays a crucial role in transforming healthcare by providing valuable insights that improve decision-making, enhance service delivery, and optimize resource use.
From predicting disease outbreaks and managing population health to improving patient access and supporting clinical research, spatial data helps healthcare systems become more proactive, efficient, and equitable.
By using geographic data, healthcare providers can better understand community needs, address disparities, and ensure resources are allocated effectively. This leads to a more resilient healthcare system that can meet current and future challenges.
Make data-driven decisions accurately with the best Power BI consulting company. Share your requirements today!
Location intelligence in healthcare uses geographic data to improve decision-making and enhance patient care. It helps optimize resource allocation by identifying areas with high healthcare needs, improve access to care by pinpointing underserved regions, and support disease outbreak predictions by analyzing geographic patterns. Additionally, it aids in facility planning, emergency response, and monitoring public health trends, ensuring that healthcare services are more efficient, targeted, and accessible to those who need them most.
The benefits of location intelligence in healthcare include improved resource allocation, better access to care, and more efficient facility planning. It helps identify underserved areas, optimize emergency response, and predict disease outbreaks. By analyzing geographic patterns, healthcare providers can target interventions, reduce health disparities, and ensure that resources are directed where they are most needed. Overall, location intelligence leads to more informed decisions, cost savings, and better health outcomes for patients.
Master quick performance fixes.
Every CTO knows the struggle of managing complex reports. The inefficiency of scattered data, the constant juggling between reporting tools, the challenge of ensuring accurate KPIs...
The very first reason why you should implement Row Level Security is to foster trust, a crucial element for any business's success. Next, it reduces data clutter and helps you load...
The performance of Power BI is significantly influenced by two essential factors: design consistency and the rapid loading of BI elements. This holds true whether you choose Tableau...