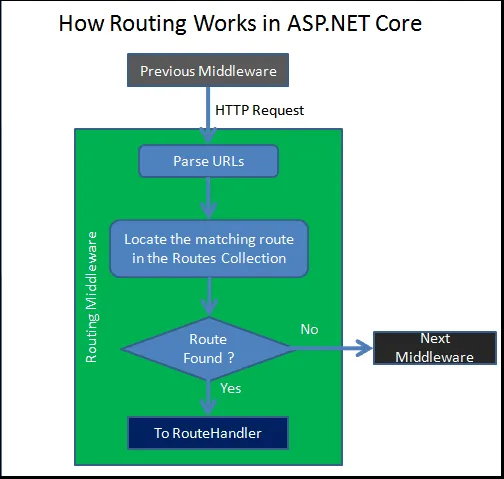
The routing is a mechanism in which it inspects the incoming Requests path and then map that request to the controllers and action methods. This mapping is done by the routing rules which are defined for the application. We can do this by add the Routing in Middleware to the request processing pipeline.
So, this Framework maps the incoming Request and URL to the Controllers action methods based on the routes configured in your application. You can configure the multiple routes for your application and for each route you can also set some specific configurations such as default values, constraints, message handlers, etc.
There are two types of routing:
- Conventional Routing
- Attribute Routing