1.Create a class
2.Inherit it from ActionFilterAttribute class
3.Override at least one of these methods:
- OnActionExecuting
- OnActionExecuted
- OnResultExecuting
- OnResultExecuted
Example:
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace WebApplication1
{
public class MyFirstCustomFilter : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnResultExecuting(ResultExecutingContext filterContext)
{
filterContext.Controller.ViewBag.GreetMesssage = "Hello World";
base.OnResultExecuting(filterContext);
}
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext)
{
var controllerName = filterContext.RouteData.Values["controller"];
var actionName = filterContext.RouteData.Values["action"];
var message = String.Format("{0} controller:{1} action:{2}", "onexecuting", controllerName, actionName);
Debug.WriteLine(message, "Action Filter Log");
base.OnActionExecuting(filterContext);
}
}
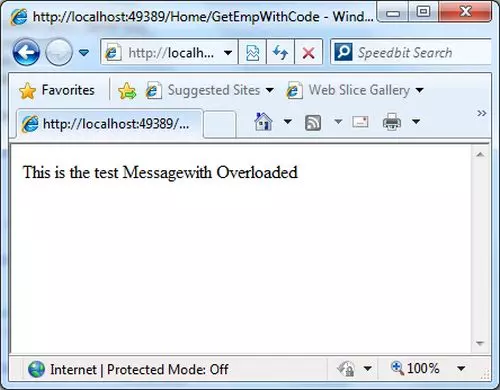
In this program, we are setting ViewBag property for the controllers being executed. The ViewBag property must be set before a controller action result is executed since we are overriding the OnResultExecuting method. Also, it is overriding OnActionExecuting to log the information about the controller’s action method.
If you want to increase the security of a certain section of your website, you can place an [Authorize] attribute on an ActionResult method in your controller. If someone visits your website and they try to hit that page and they aren't authorized, they are sent to the login page (Of course, you need to modify your web.config to point to the login page for this to work properly).
public class RequiresAuthenticationAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
var httpContext = context.HttpContext;
if (!httpContext.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
if (httpContext.Request.Url != null)
{
var redirectOnSuccess = httpContext.Request.Url.AbsolutePath;
var urlHelper = new UrlHelper(context.RequestContext);
var url = urlHelper.LoginUrl(redirectOnSuccess);
httpContext.Response.Redirect(url, true);
}
}
base.OnActionExecuting(context);
}
}
Possible levels of Action Filters
1. As Global Filter
A filter can be added to the global filter in App_Start\FilterConfig. After applying this, one can use this for all the controllers in the Application.
public class FilterConfig
{
public static void RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilterCollection filters)
{
filters.Add(new HandleErrorAttribute());
filters.Add(new MyFirstCustomFilter());
}
}
2. At Controller Level
To apply the filter at the controller level, we should apply it as an attribute to a controller. At the time of applying to the controller level, action will be available to all controllers.
[MyFirstCustomFilter]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
3. At Action Level
To apply the filter at the action level, we should apply it as an attribute of the action.