Factors that ensure Java’s continued dominance
The following are some of the factors that keep Java at the top.
#1 The use case for Java
Most comparisons between JavaScript and Java, including Python and Java, lack the context of the use case for which both languages are best suited. The application backend is Java's strong suit. It is where business logic is built, procedures are implemented, and complicated sets of objects interact.
When it comes to developing medium or big pieces of software, Java is still the preferred backend platform. You won't find many Python or JavaScript backends in major programs operating in banks or insurance businesses, for example. In an enterprise application, when 80% of the application logic is developed in the backend, Java is still unquestionably preferable. You'll see a python AI-ML-based library being incorporated in the same application, but that's not where a lot of work and money is spent. The same can be said about JavaScript, which is typically used to construct frontends with frameworks and modules like Angular and React. However, the emphasis remains on the backend. And this is reflected in the team compositions.
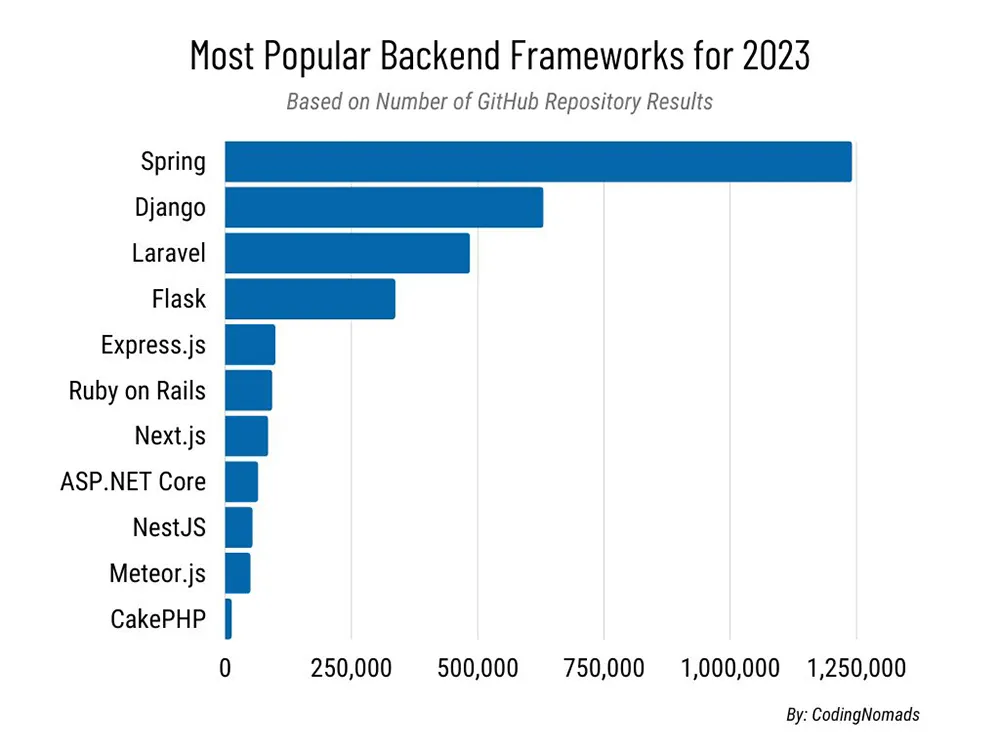
If you look at a team provided with developing medium to big apps, you'll see a majority of programmers in the team have backend Java abilities. NodeJS is a strong rival in this arena, although Java retains the advantage due to one or more of the factors listed below.
#2 Java has a Vast ecosystem.
The ecosystem around a language plays a major role in what a language can deliver. Java has decades of a head start as compared to other languages in this case. There are major industry forums and corporate players who are deeply invested in making the Java ecosystem stronger. For example, Apache Foundation, and Spring ecosystem backed by VMWare to name a few.
1. Libraries and frameworks: Java has a vast collection of libraries and frameworks that are actively maintained by the community. These libraries and frameworks help developers to build applications more efficiently and with less code. Examples of popular Java frameworks include Spring, Hibernate, and Quarkus.
2. Platforms: Using Java, developers can build applications for a variety of platforms, including web applications, mobile applications, enterprise applications, and desktop applications. This means that Java developers can build a wide range of applications using the same language.
3. Tools Java has a wide range of tools for development, debugging, and testing. For example, Eclipse and IntelliJ IDEA are popular integrated development environments (IDEs) for Java development. JUnit is a popular testing framework for Java, and tools like Maven and Gradle are used for building and managing Java projects.
4. Community: Java has a large and active community of developers who contribute to the language, tools, and libraries. This means that developers can get help, share their knowledge, and collaborate on projects more easily.
5. Enterprise support: For enterprises that require enterprise support for mission-critical applications, there are various service providers that can provide support and timely delivery of security fixes. Companies such as IBM, Oracle, and Red Hat, for example, provide enterprise support for Java and related technologies.
Overall, the vast ecosystem of Java makes it a versatile and powerful language for building a wide range of applications. The large community and enterprise support also ensure that Java will continue to be a relevant and widely used language for years to come.
#3 Java is both efficient and widely used.
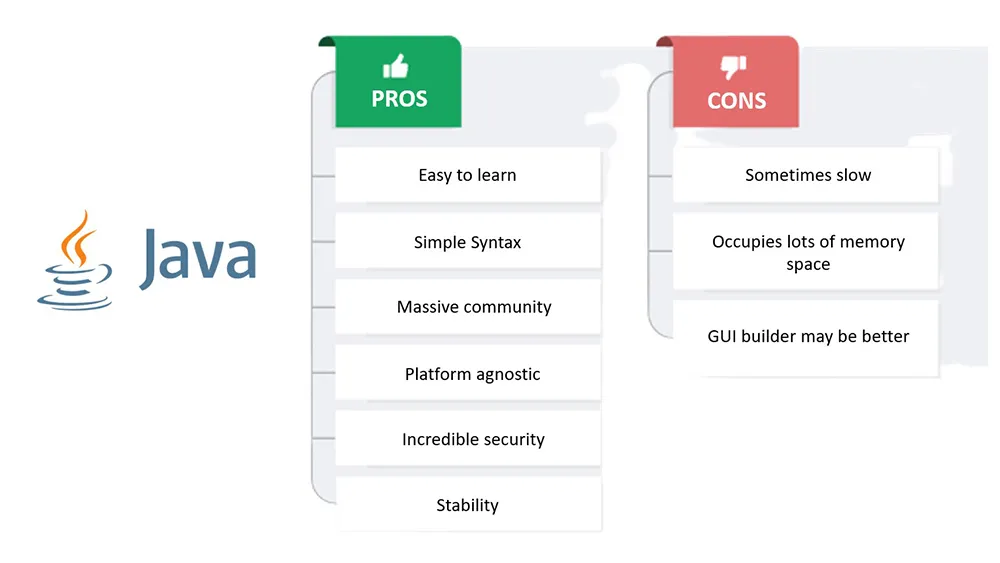
Java is one of the most efficient programming languages in the world today (keeping the use case in mind). It is extensively used in diverse industry verticals due to its flawless features and breakless security.
It may surprise you to find that Java was the top programming platform in 2020 and fifth in 2023 and consumes fewer resources to accomplish tasks compared to other languages.
Besides, it uses less electricity and hence is more environment-friendly by far when compared to JavaScript (Node), Python, and C#. The only place where Java lags as per these results is memory consumption, but Java has new-age solutions for that too.
#4 Java has first-class support to build cloud-native applications
In recent years, cloud computing has become increasingly popular for businesses looking to build and deploy their applications using cloud infrastructure (on-prem or public). Cloud-native development involves building applications that are specifically designed to run on cloud infrastructure, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Java has long been a popular language for building enterprise applications that were monolithic, and it has now become a popular choice for building cloud-native applications that use microservice architecture. One of the main reasons for this is the first-class support that Java provides for cloud-native development and microservices.
Using Java, developers can quickly build REST-based microservices using tools like Spring-boot and Spring Cloud from Spring Framework (supported by VMWare) or the tools like Weld (supported by RedHat).
One of the biggest complaints from the cloud-native community against Java has been the size of the bare minimum libraries that are required to run Java was too big. Java community and ecosystem have addressed that problem by offering cloud-native alternatives like Quarkus and GraalVM
#5 Rapid innovation and support from major tech companies
Java continues to evolve and innovate rapidly with major corporations like Oracle, and Amazon having their distributions while companies like Microsoft, Google, and Redhat support the adoption via Adoptium . As a result, Java as a platform has seen more frequent releases with each release adding features that help Java tackle new-age problems with reliability. Some of the major innovations like Project loom and Project Valhalla along with project amber should be looked at.
Whether you are a developer who wants to make your career future-proof or a business that wants to invest in technology that will give maximum ROI for a long time, Java is the right bet.