Ethical Considerations for Using AI in Healthcare Software
Let’s keep it simple. In healthcare, trust, safety, and human dignity come first, no matter what solution you build. The same applies to AI. Today, it is everywhere, from clinics...
Listening is fun too.
Straighten your back and cherish with coffee - PLAY !
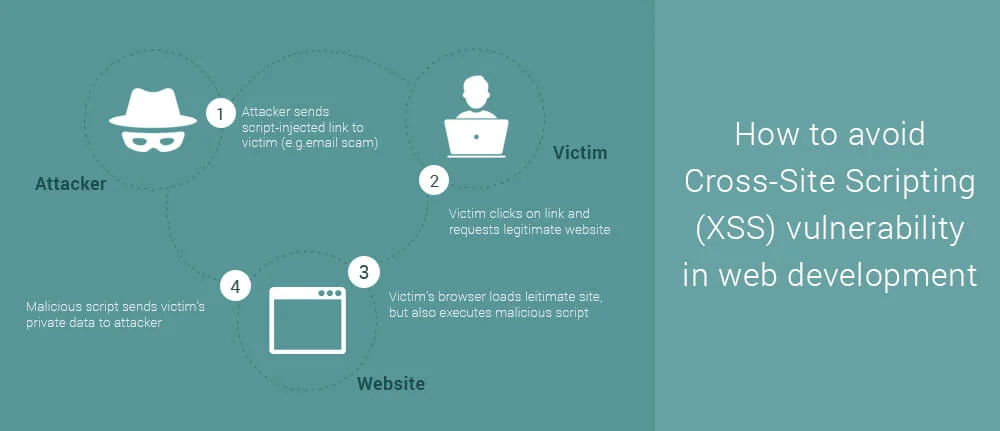
Cross-site scripting is ranked 3rd in the list of OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities 2017. Cross-site scripting are one of the most rampant occurring injection attacks faced by various web application across businesses. That’s why to know the causes of XSS, its impact and prevention is must.
Cross-site scripting attacks are types of injection, in which malicious scripts are injected into trusted web applications. This attack happens when a hacker uses web application to send infected code, many times in the form of a browser side script to the remote end user. Flaws which allow these attacks to succeed are widespread and can occur anywhere. A website uses input from a user and within an output it generates without encoding or validating it.
An attacker uses XSS to send a malicious script to victim. The end user’s browser doesn’t have any way to know the trustworthiness of the script. The user believes that the script has come from trusted source so he executes it. The malicious script in it gets all the sensitive information retained by browser like session id, tokens, cookies, etc. These kinds of scripts even rewrite the content of HTML page.
Cross-site scripting has three types.
Reflected XSS: An attacker sends a link to a target application through some social media or email. This link contains an embedded script which are executed while visiting script.
Stored XSS: An attacker is able to plant a persistent script into target website which executes when anyone visits it.
In today’s world where every industry moving towards digitization, attackers also are keeping owl eyes breaking them in easiest way. A website for a company is the first image for customers. So, it has become mandatory for web developers to take precautions for various web application attacks and making it secured from attackers.

Let’s keep it simple. In healthcare, trust, safety, and human dignity come first, no matter what solution you build. The same applies to AI. Today, it is everywhere, from clinics...

Let's keep it real. The whole point of building autonomous Agents is to cut manual work and keep focus on business. Approvals that used to take days can happen in hours because...

Remember our last guide - Power BI forecasting? It revealed things that truly blocks accuracy, both structural and situational. Now it's time to take the next step. Knowing Power...