How to Do Forecasting in Power BI (Steps & Accuracy Metrics)
Remember our last guide - Power BI forecasting? It revealed things that truly blocks accuracy, both structural and situational. Now it's time to take the next step. Knowing Power...
Listening is fun too.
Straighten your back and cherish with coffee - PLAY !
Over the past couple of years, Blockchain technology has proved that it is one of the most promising developments of the time, one that has the potential to disrupt more than just the financial sector. As technology started to grow, many esteemed Blockchain Software development companies have started to adopt this technology for Smart contract projects in large numbers. Blockchain is such a technology that has thrashed the ideas of hacking by underpinning with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The Blockchain is a buzzword that you keep hearing these days. In this technology era, Bitcoin and Blockchain are reaching technology acumen as preferred technology for implementing various business solutions. Most of the industries and even the government is considering Blockchain adoption. Generally, people might get confused with Blockchain and Bitcoin. Bitcoin is an electronic cryptocurrency that is used for online payment without the need for a third-party while blockchain is the platform and framework to make every transaction transparent and immutable. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is open for everyone and anyone can join this network. We can say that the initial step of blockchain technology is bitcoin.
Bitcoin is firstly introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 (Michael Crosby, 2015 ). Satoshi Nakamoto was an anonymous person or group of people who started working on the Bitcoin concept in 2007. They registered the Bitcoin.org domain on 18th August. Soon after on 31st October, they published a whitepaper which described bitcoin, proof-of-work, transaction process, etc. The First Bitcoin project was registered at SourceForge.net on 09th November 2008. The Genesis Block or Block 0 was established on January 3rd, 2009, at 18:15:05 GMT. After 6 days, i.e., on 9th January, Version 0.1 of bitcoin was released and the mining process was initiated. The first bitcoin transaction occurred between Satoshi and Hal Finney on January 12th, 2009. ( Michael Crosby, 2015 )
Blockchain is not just about coins and tokens. Blockchain technology is more than cryptocurrency.
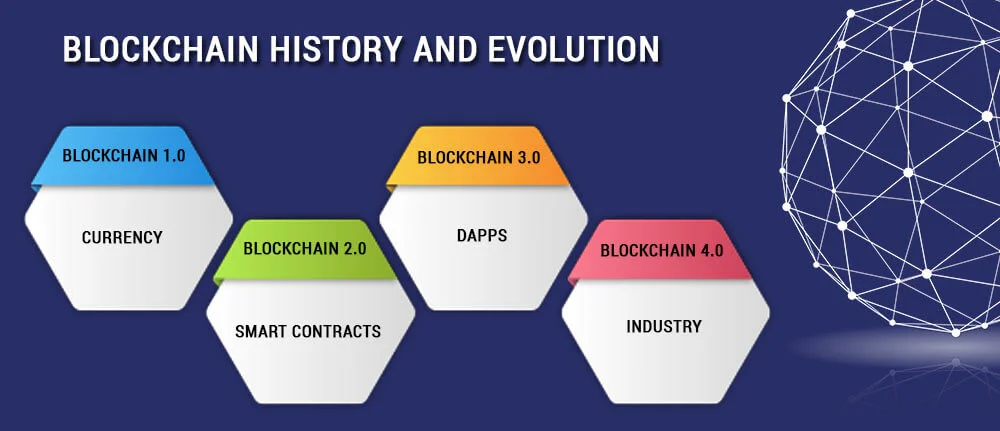
Here is the evolution of blockchain technology and versioning from v1.0 to v4.0 is available at (https://medium.com/@UnibrightIO)
Blockchain 1.0: Currency
Blockchain 2.0: Smart Contracts
Blockchain 3.0: DApps
Blockchain 4.0: Making blockchain usable in the industry
The first application of blockchain technology was Blockchain 1.0 in 2009, hence it is v1.0. Cryptocurrencies are the implementation of blockchain 1.0. Blockchain allows financial transactions. Cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange, created and stored electronically in the Blockchain using encryption techniques to control the creation of money and allow for verification of funds transfer. When blockchain and cryptocurrency technology first came to the market, one of the primary functions was to eliminate third party interaction in all kinds of currency transfer. It was the era when economies started making the shift from paper currency to primarily digital currency.
One issue with digital currency was the double-spending problem. Digital currency does not exist physically, so there was some tricky issue that an accurate and real-time record needs to be kept. Blockchain technology solved this problem as it is the open public ledger so all transactions are chronologically recorded as a block in the blockchain network and each block has its own timestamp to ensure that the same value is not copied.
Smart Contracts are the new and efficient concept of blockchain technology. Smart contracts are the small computer programs or pre-written logic that exist in the blockchain. They are self-ruling computer programs that execute automatically. Smart contracts trigger automatically when some conditions get fulfilled. One of the biggest advantages of this technology is that no one can tamper with smart contracts. Smart Contracts reduce the cost of execution and verification. It prevents fraud and allows transparent contracts.
DApp is an abbreviation of decentralized application, which means no centralization. DApp has decentralized storage. The Decentralized app has its backend code running on its decentralized node while in a traditional app has its backend code running on centralized servers. DApp has frontend developed using any programming languages that can make calls to its backend through APIs, like a traditional app. On the other hand, the Decentralized app has its frontend hosted on decentralized storages such as Ethereum Swarm. DApps are the combination of frontend and contracts, here contracts are decentralized logic.
Blockchain 4.0 provides solutions and approaches that make blockchain consulting companies applicable to fulfill business demands. Automation, enterprise resource planning, and integration of different execution systems are the key features of Industries. Still, the industrial revolution demands the highest degree of trust and privacy; here Blockchain comes for the rescue. Few areas in which blockchain is useful, for example, financial transactions, Supply chain management, condition-based payments, IoT data collection, health management, and asset management. Blockchain 4.0 means, making Blockchain 3.0 applicable in real-life business.
(n.d.). Retrieved from https://medium.com/@UnibrightIO.
(n.d.). Retrieved from https://urbancrypto.com/cryptocurrency.
Michael Crosby, . G. (2015 ). Sutardja Center for Entrepreneurship & Technology Technical Report .

Remember our last guide - Power BI forecasting? It revealed things that truly blocks accuracy, both structural and situational. Now it's time to take the next step. Knowing Power...

It's amazing to see how Data teams today are racing ahead - moving from traditional warehouses to cloud-native platforms, lakehouses, and real-time architectures. But in this rush,...

Think about the last time CTOs spent most of their time fixing old systems. Updates were slow, servers were expensive, and adding new features took time. Now, things have changed....